Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Idomura, Yasuhiro
Physics of Plasmas, 24(8), p.080701_1 - 080701_5, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:46.05(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)An electron heating modulation numerical experiment based on a global full-f gyrokinetic model shows that transitions from ion temperature gradient driven (ITG) turbulence to trapped electron mode (TEM) turbulence induced by electron heating generate density peaking and rotation changes. Toroidal angular momentum balance during the rotation changes is revealed by direct observation of toroidal angular momentum conservation, in which in addition to ion turbulent stress, ion neoclassical stress, radial currents, and toroidal field stress of ions and electrons are important. Toroidal torque flipping between ITG and TEM phases is found to be related to reversal of the ion radial current that indicates coupling of particle and momentum transport channels. The ion and electron radial currents are balanced to satisfy the ambipolar condition, and the electron radial current is cancelled by the electron toroidal field stress, which indirectly affects toroidal torque.
 n waves in tokamaks
n waves in tokamaksBierwage, A.; Shinohara, Koji
Physics of Plasmas, 21(11), p.112116_1 - 112116_21, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:72.13(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Takizuka, Tomonori; Hosokawa, Masanari*
Contributions to Plasma Physics, 46(7-9), p.698 - 703, 2006/09
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:43.86(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Enhanced heat and particle fluxes to the divertor plates after an ELM crash in H-mode plasmas are the crucial issues for the tokamak reactor operation. Kinetic effect in the transient behaviour of SOL-divertor plasmas for this case is not yet well known. We investigate above problems with an advanced particle simulation code, PARASOL. Dependence of the particle and heat propagations on the collisionality is studied systematically. Effect of the particle recycling is also studied.
Matsumoto, Taro; Naito, Hiroshi*; Tokuda, Shinji; Kishimoto, Yasuaki*
Nuclear Fusion, 45(11), p.1264 - 1270, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:43.63(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A gyrokinetic particle simulation is executed to clarify the effect of the electron inertia on the MHD phenomena in the reversed shear configuration (RSC) of a cylindrical tokamak plasma. It is found that the collisionless (kinetic) double tearing modes grow up at the Alfv n time scale, and nonlinearly induce the internal collapse when the helical flux at the magnetic axis is less than that at the outer resonant surface. After the internal collapse, the secondary reconnection is induced by the current concentration due to the
n time scale, and nonlinearly induce the internal collapse when the helical flux at the magnetic axis is less than that at the outer resonant surface. After the internal collapse, the secondary reconnection is induced by the current concentration due to the 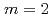 convective flow. It is also clarified that a nonlinear dynamics accompanied with the elementary processes caused by the
convective flow. It is also clarified that a nonlinear dynamics accompanied with the elementary processes caused by the 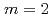 flow can generate a new RSC with resonant surfaces. In the presence of the density gradient, after the full reconnection induced by the
flow can generate a new RSC with resonant surfaces. In the presence of the density gradient, after the full reconnection induced by the 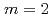 mode, the radial electric field is found to be generated due to the difference of the
mode, the radial electric field is found to be generated due to the difference of the 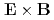 motion between ions and electrons. However, the intensity of the radial field is not so large as that induced by the collisionless kink mode.
motion between ions and electrons. However, the intensity of the radial field is not so large as that induced by the collisionless kink mode.
Matsumoto, Taro; Naito, Hiroshi*; Tokuda, Shinji; Kishimoto, Yasuaki
Physics of Plasmas, 12(9), p.092505_1 - 092505_7, 2005/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.86(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The behavior of the collisionless magnetohydrodynamics modes is investigated by the gyro-kinetic particle simulation in a cylindrical tokamak plasma in the parameter region where the effects of electron inertia and electron parallel compressibility are competitive for magnetic reconnection. Although the linear growth of the 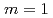 internal kink-tearing mode is dominated by the electron inertia, it is found that the growth rate can be nonlinearly accelerated due to the electron parallel compressibility proportional to the ion sound Larmor radius
internal kink-tearing mode is dominated by the electron inertia, it is found that the growth rate can be nonlinearly accelerated due to the electron parallel compressibility proportional to the ion sound Larmor radius 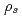 . It is also found that, as decreasing the electron skin depth
. It is also found that, as decreasing the electron skin depth 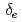 , the maximum growth rate before the internal collapse saturates independently of the microscopic scales such as
, the maximum growth rate before the internal collapse saturates independently of the microscopic scales such as 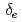 and
and 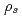 . The acceleration of growth rate is also observed in the nonlinear phase of the
. The acceleration of growth rate is also observed in the nonlinear phase of the 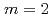 double tearing mode.
double tearing mode.
Utsumi, Takayuki*; Matsukado, Koji*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Bulanov, S. V.*
Applied Physics A, 79(4-6), p.1185 - 1187, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:40.13(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Kishimoto, Yasuaki
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 80(5), p.390 - 395, 2004/05
High performance magnetically confined plasma is realized by having structures in plasmas, where different elementary processes with different time and spatial scales are deeply contributing with each other. A research based on large scale simulation is then essential to understand such hierarchical complex plasmas. We discuss the underlying physical process of the structural plasma and present a prospect for future numerical simulations covering a wide dynamical range.
Kishimoto, Yasuaki
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 79(5), p.460 - 463, 2003/05
This is a collection of review article related to the "Multiple Time and Spatial Scale Plasma Simulation" of various fields including fundamental research area of self-organization, magnetic and laser fusion field, space and astrophysics field where a plasma plays an essential roles.
Takizuka, Tomonori; Hosokawa, Masanari*; Shimizu, Katsuhiro
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 313-316(1-3), p.1331 - 1334, 2003/03
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:69.06(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In course of tokamak fusion research, particle and heat control is one of the most crucial issues. Helium ash exhaust and impurity retention in the divertor region owe to the plasma flow towards divertor plate. The localization of heat load on the plate depends on the flow pattern. Accordingly, particle and heat control can be achieved by the proper control of the flow in SOL and divertor plasmas. In this paper, the flow control is studied with two-dimensional particle simulations by PARASOL (PARticle Advanced simulation for SOL and divertor plasmas) code. Magnetic field configuration with separatrix like a tokamak divertor configuration is given. Hot particle source is put in the core plasma. Recycling cold particle source is located near the divertor plate. Particle source of gas puff in the SOL plasma is given for the flow control. Divertor biasing is available by changing the electrostatic potential on the plates. Effects of gas puff and biasing on the flow are studied. Controllability is evaluated from simulation results.
Matsumoto, Taro; Tokuda, Shinji; Kishimoto, Yasuaki; Naito, Hiroshi*
Physics of Plasmas, 10(1), p.195 - 203, 2003/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:16.93(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Effects of density gradient on the collisionless m=1 internal kink mode in a cylindrical tokamak plasma are studied by the gyro-kinetic particle simulations. When the density gradient is not large enough to change the full reconnection process, the phenomena after the full reconnection, such as the secondary reconnection and the evolution of the safety factor profile, are changed considerably due to the self-generated radial electric field, i.e. the m=0 mode. The growing mechanism is explained by the difference of 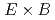 drift motion between ions and electrons, which is caused by the fast parallel motion of electron. Once the radial electric field is triggered by the symmetrical flow induced by the m=1 mode, the m=0 mode grows up to the same level as the m=1 mode, and drives an
drift motion between ions and electrons, which is caused by the fast parallel motion of electron. Once the radial electric field is triggered by the symmetrical flow induced by the m=1 mode, the m=0 mode grows up to the same level as the m=1 mode, and drives an 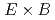 plasma rotation in the ion diamagnetic direction, which breaks the symmetrical plasma flow induced by the m=1 mode. The density and current distributions, and minimum safety factor after the full reconnection, are found to be affected by the asymmetrical flow driven by the m=1 and m=0 modes.
plasma rotation in the ion diamagnetic direction, which breaks the symmetrical plasma flow induced by the m=1 mode. The density and current distributions, and minimum safety factor after the full reconnection, are found to be affected by the asymmetrical flow driven by the m=1 and m=0 modes.
Bruskin, L. G.; Mase, Atsushi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 71(5), p.1274 - 1279, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:29.24(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The results of analytical solution of the time-dependent 2D full wave equation in cylindrical coordinates are presented here with application to plasma fluctuation reflectometry. We consider a family of plasma density profiles with cylindrical symmetry, which allow for a full integrationof the microwave scattering problem in Born approximation. Based on the results of analytical modeling, the effects of beam refraction and scattering are studied taking into account possible asymmetries such as antenna misalignments and movement of plasma fluctuations. It is shown that the reflectometer sensitivity to the small radial scale fluctuations increases in the plasma with the high curvature. It is also noted that the microwave reflectometry measurements are better localized in high curvature plasmas.
Bruskin, L. G.; Mase, Atsushi*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 72(11), p.4139 - 4144, 2001/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Utsumi, Takayuki*; Sasaki, Akira; Kunugi, Tomoaki*; Fujii, Sadao*; Akamatsu, Mikio*
Proceedings of 4th International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications (SNA 2000) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2000/09
no abstracts in English
Polevoi, A. R.; Nishio, Satoshi; Ushigusa, Kenkichi
JAERI-Tech 2000-001, p.16 - 0, 2000/01
no abstracts in English
Utsumi, Takayuki*; Sasaki, Akira
Nihon Ryutai Rikigakkai Nenkai 2000 Houbunshu, 2 Pages, 2000/00
no abstracts in English
Utsumi, Takayuki*; Sasaki, Akira; Kunugi, Tomoaki*; Fujii, Sadao*; Akamatsu, Mikio*
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on High-Power Particle Beams (BEAMS 2000) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2000/00
no abstracts in English
Yamagiwa, Mitsuru; Koga, J. K.; L.N.Tsintsadze*; Ueshima, Yutaka*; Kishimoto, Yasuaki
Physical Review E, 60(5), p.5987 - 5990, 1999/11
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:62.99(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Yamagiwa, Mitsuru; Koga, J. K.; Sagisaka, Akito*
Journal of Physics B; Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics, 32(12), p.2881 - 2887, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Optics)no abstracts in English
Yamagiwa, Mitsuru; Koga, J. K.
Journal of Physics D; Applied Physics, 32(19), p.2526 - 2528, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:67.9(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Matsumoto, Taro; Tokuda, Shinji; Kishimoto, Yasuaki; Takizuka, Tomonori; Naito, Hiroshi*
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.2, p.97 - 100, 1999/00
no abstracts in English